Unit 7 – Triangles: Sums of angles, length/side relationships, determining if three lengths form a triangle
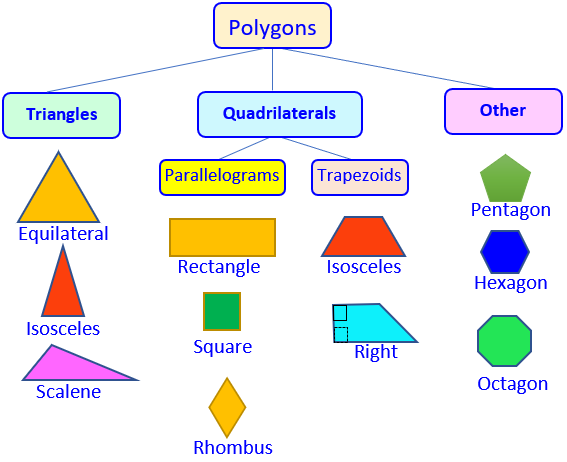
Triangles
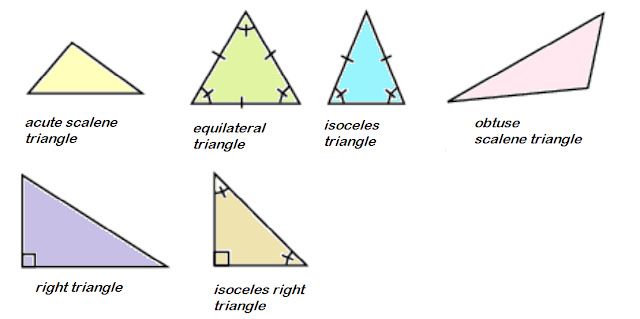
Scalene. No equal sides nor angles
Isosceles. Two equal sides and 2 equal angles
Equilateral. 3 equal sides and 3 equal angles which are 600 each.
Right. 1 right angle, 2 acute angles
Acute. 3 acute angles
Obtuse. 1 obtuse angle, 2 acute angles
The interior angles of a triangle always add up to 180°
Triangle Properties
- The sum of all the angles of a triangle is equal to 1800.
- The sum of the length of the two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
- The difference between the two sides of a triangle is less than the length of the third side.
- The side opposite the greater angle is the longest side of all the three sides of a triangle.
- The exterior angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles. This property of a triangle is called an exterior angle property
- Two triangles are said to be similar if their corresponding angles of both triangles are congruent and the lengths of their sides are proportional.
- Area of a triangle = ½ × Base × Height
- The perimeter of a triangle = sum of all its three sides
Understandings:
- Understand that the sum of the interior angle measures of a triangle is 360°.
- Understand how to classify triangles as acute, equiangular, right, and obtuse.
- Understand how to classify triangles as scalene, isosceles, and equilateral.
- Understand that an exterior angle is equal to the sum of its remote interior angles.
- Triangle inequality theorem: the sum of 2 sides of a triangle must be greater than the third side.
Vocabulary:
Triangle: A triangle is a closed figure made up of three line segments.
Acute Triangle: A triangle with three acute angles. (All angles must be less than 90 degrees)
Right Triangle: A triangle with one right triangle. (One angle with 90 degrees)
Obtuse Triangle: A triangle with one obtuse angle. (One angle greater than 90 degrees)
Equiangular Triangle: A triangle with all ANGLES equal.
Equilateral Triangle: A triangle with all SIDES equal.
Scalene Triangle: A triangle with NO congruent sides. (Sides are all different lengths)
Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with TWO congruent sides. (Two sides are equal to each other)
“I can” Statements
- I can calculate perimeter and area of a triangle.
- I can calculate perimeter and area of a parallelogram.
- I can describe what happens to the perimeter and area of a 2D shape when the lengths of the sides are doubled.
- I can construct triangles from three measures of angles or sides.
- I can draw (freehand, with ruler and protractor, with technology) geometric shapes with given conditions.
- I can notice when the given conditions determine a unique triangle, more than one triangle, or no triangle.